Demystifying Reverse Engineering: Unveiling the Secrets of Technological Exploration

SKILLABLE INDIA
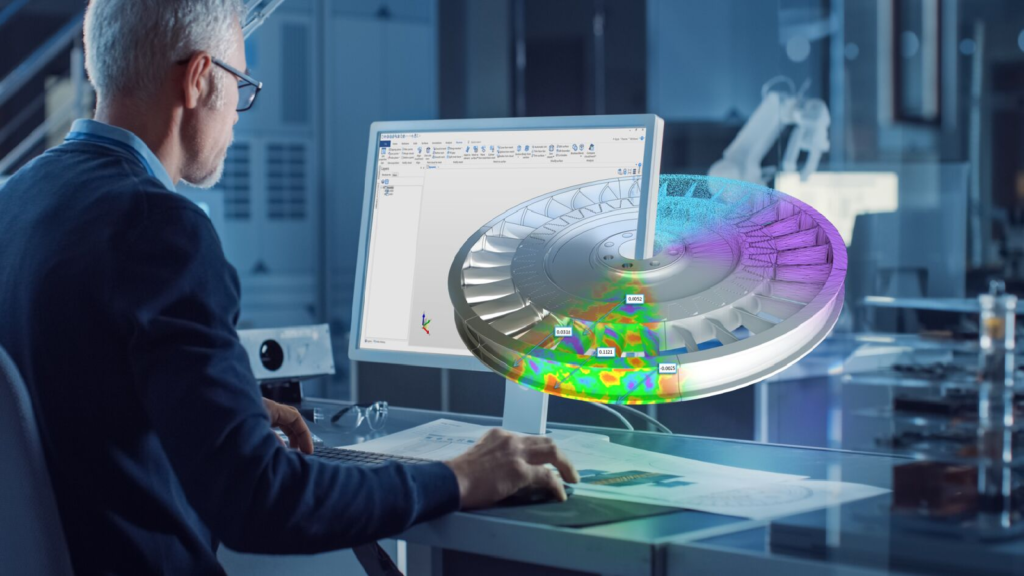
Reverse engineering is a fascinating and essential discipline in the world of technology. It involves the process of deconstructing and analyzing a product or system to understand its design, functionality, and inner workings. By unraveling the mysteries of how something is built, reverse engineering enables us to gain valuable insights, improve existing systems, and develop innovative solutions. It plays a crucial role in various fields, including software development, intellectual property protection, product design, and security analysis. With its power to uncover hidden knowledge and drive innovation, reverse engineering is a cornerstone of technological exploration.
What is reverse engineering?
Reverse engineering involves the process of disassembling and analyzing a product or system in order to understand its design, functionality, and internal workings. By deconstructing and exploring various components and their interactions, reverse engineers gain valuable insights that can be applied to improve existing systems or develop innovative solutions.
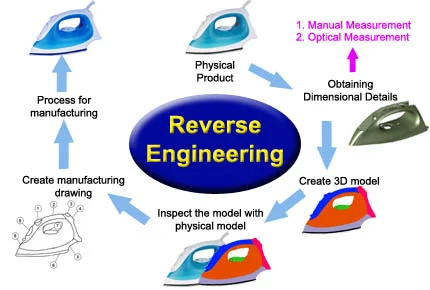
1. Motivations behind reverse engineering:
Reverse engineering is driven by a variety of motivations, including:
Understanding legacy systems: When documentation or source code is unavailable, reverse engineering enables the understanding and maintenance of legacy systems.
Increasing competitiveness: By reverse engineering competing products, companies can gain insight into their features and functionalities, allowing them to enhance their own products or create innovative alternatives.
Security Vulnerability Detection: Reverse engineering helps identify potential vulnerabilities and vulnerabilities in software applications or hardware devices, thereby helping organizations strengthen their security measures.
2. Reverse engineering process:
Reverse engineering involves a series of steps:
Research and Documentation: Gather relevant information about the target system, including technical specifications, patents, and available documentation.
Analysis and Disassembly: Breaking down a system, either physically or through software analysis, in order to understand its components and their interrelationships.
Reconstruction and model building: Using the knowledge gained during the analysis phase to reconstruct models or representations of the original design.
Functional Testing and Verification: Validating the accuracy of the reverse-engineered model, testing the reconstructed system to ensure that its behavior aligns with the original.
Tools and techniques used in reverse engineering:
Reverse engineering uses a variety of tools and techniques, such as:
3. Disassemblers: Software tools that convert machine code into human-readable assembly language representation.
Debuggers: Tools that aid in analyzing and debugging software by step-by-step execution of code and inspection of memory conditions.
Decompilers: Software tools that translate compiled code back into a high-level programming language representation.
Applications of reverse engineering:
Reverse engineering has applications in many areas:
4. Software development and maintenance: Reverse engineering helps in understanding and improving existing software applications, ensuring compatibility and code interoperability.
Intellectual Property Protection: It helps to identify and remedy intellectual property infringements, protect innovations and protect proprietary technologies.
Product design and innovation: By reverse engineering products, companies gain insight into their design, functionality, and market position, facilitating the development of improved or alternative solutions.
Security analysis: Reverse engineering helps locate security vulnerabilities, allowing organizations to patch vulnerabilities and fortify their systems against potential threats.
5. Legal and Ethical Considerations:
While reverse engineering serves valuable purposes, it is important to be mindful of the legal and ethical limitations. Respect intellectual property rights, comply with licensing agreements and engage in reverse engineering activities within the scope of applicable laws and regulations.
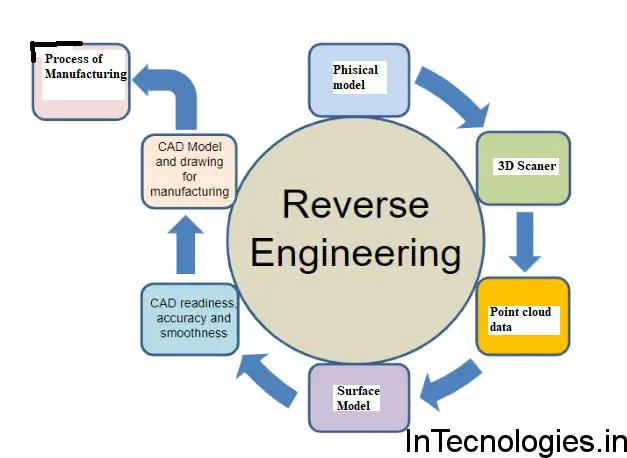
Conclusion:
Reverse engineering is an indispensable discipline that enables us to go deep into the inner workings of technology. By adopting a process of deconstruction, analysis, and reconstruction, we gain valuable insights that can fuel innovation, increase security, and improve existing systems. As technology continues to evolve, reverse engineering will continue to be an important tool in unlocking the secrets of the digital landscape.
So, let us embark on this journey of exploration, embrace the wonders of reverse engineering and take advantage of its potential to unlock hidden treasures.
Book a Free Demo, now!
Know more about our Engineering courses with Job Assistance!


